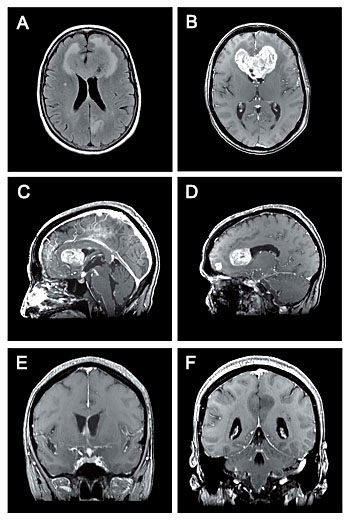
 |
predominantly
hypointense signal in T1 and hyperintense in T2 with a few areas of
necrosis. Some of the lesions strongly enhanced following gadolinium
injection, while one lesion in the left parietal paramedien area did not
enhance. (Fig1 A,B,C,D) The lesion was associated with surrounding
vasogenic edema and causing severe mass effect resulting in compression of
the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles. A multitude of small additional
lesions were also noted within the cerebral hemispheres and leptomeningeal
spaces. (Fig1 E,F)
Figure 1. A, Axial FLAIR image showing a hyperintense heterogeneous mass
crossing the corpus callosum with marked associated vasogenic edema. There
is a hyperintense cortical thickening in the left precuneus without edema.
B, Axial T1 weighted image with contrast demonstrating enhancement of the
lesion. C, Sagittal T1 weighted image with contrast showing small areas of
nodular enhancement medially in a subependymal location along the left
lateral ventricle. The infundibulum and the hypothalamus are widened and
enhancing. There is enhancement of the leptomeninges over the anterior
surface of the brainstem and most marked at the level of the interpeduncular
fossa. D, Sagittal T1 weighted image with contrast showing an other small
enhancing lesion in the right frontal lobe.
E, Coronal T1 weighted image
with contrast showing the enhancement in the infundibulum.
F, Coronal T1
weighted image with contrast showing no enhancement of the lesion in the
left precuneus. There is diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement infratentorially.
|