|
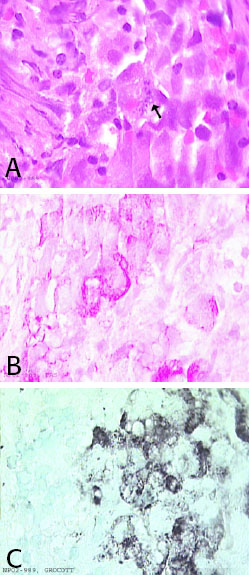 Hematoxylin/eosin
stain shows epithelioid type cells with sightly vacuolated eosinophilic
cytoplasm and large nuclei. One cell contains small rod like structures
with indistinct borders (figure A). These cells present a strong
cytoplasmic reactivity with the PAS stain (figure B). Grocoot stain
reveals an intracytoplasmic positivity within the PAS positive cells
(figure C). Immunohistochemistry to further characterized these cells
showed the cells to be positive for CD68 (macrophage type cell marker),
negative for cytokeratin, LCA, GFAP and CD1a. FITE stain for mycobacterium
and Gram stain were negative. These findings are compatible with the
histological diagnosis of cerebral Whipple’s disease. Hematoxylin/eosin
stain shows epithelioid type cells with sightly vacuolated eosinophilic
cytoplasm and large nuclei. One cell contains small rod like structures
with indistinct borders (figure A). These cells present a strong
cytoplasmic reactivity with the PAS stain (figure B). Grocoot stain
reveals an intracytoplasmic positivity within the PAS positive cells
(figure C). Immunohistochemistry to further characterized these cells
showed the cells to be positive for CD68 (macrophage type cell marker),
negative for cytokeratin, LCA, GFAP and CD1a. FITE stain for mycobacterium
and Gram stain were negative. These findings are compatible with the
histological diagnosis of cerebral Whipple’s disease.
In order to confirm the diagnosis, less than 300µl of
intra-ventricular fluid removed during surgery and CSF were sent for
molecular diagnosis. PCR using specific primers for T. Whippellii was
negative. PCR using universal bacterial primers revealed the presence of a
very faint band for 16SrRNA but sequencing was not possible.
Immunohistochemistry for T. Whippellii was performed on the section and
was negative (courtesy of Dr. Leipidi, Marseille, France). Electron
microscopy performed on deparaffinized tissue was inconclusive. An
intestinal biopsy was performed and showed no pathology. PCR was also
negative.
Ref: Scandinavian Journal of infection Diseases, 1999, 31, 411-4.
Fig. 4 |
 |
|